We usually associate drought with summer – with parched lawns, wilting plants, and the need for frequent watering. However, we must remember that the problem of soil water deficiency affects all seasons. Although autumn is often perceived as a time of frequent rains and a respite from gardening, it is actually a crucial time to prepare the garden and farm for the coming season. Now is the time to take steps to better retain water, store it, and improve plant health in the coming months.
Tag Archives: drought in Poland
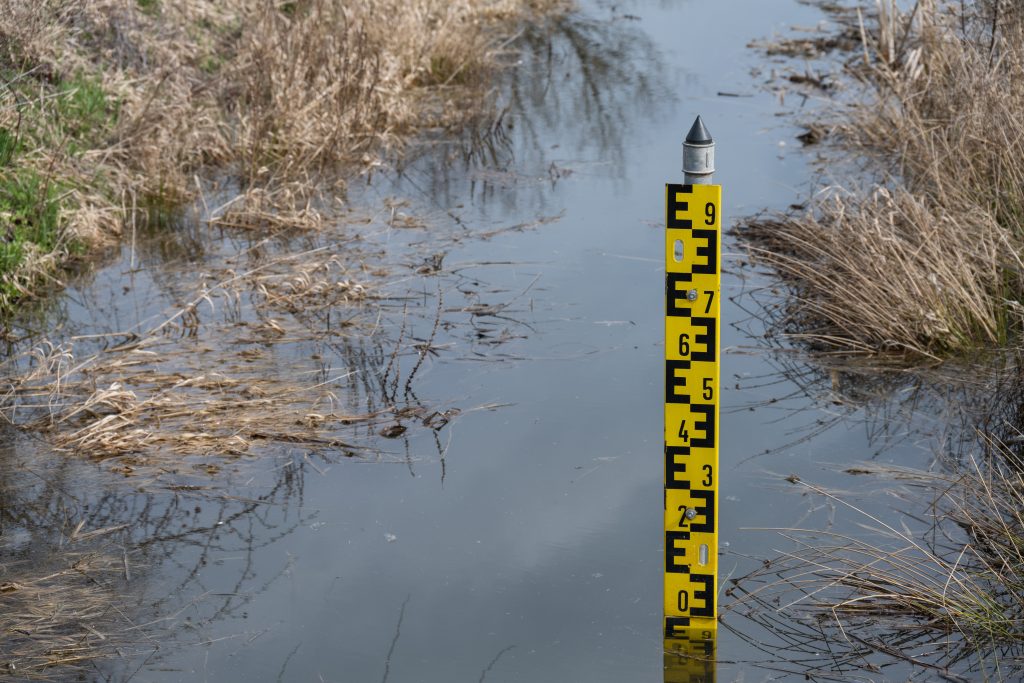
The summer of 2025 was a particularly contrasting period in Poland in terms of water balance. Although the water balance indicator itself is complex and takes into account both inflows (including atmospheric precipitation, surface and groundwater recharge) and losses (evaporation, plant transpiration, surface runoff), in practice its development depends primarily on precipitation and air temperature, which influences the intensity of evapotranspiration (including evaporation from soil surfaces and water bodies, as well as plant transpiration).
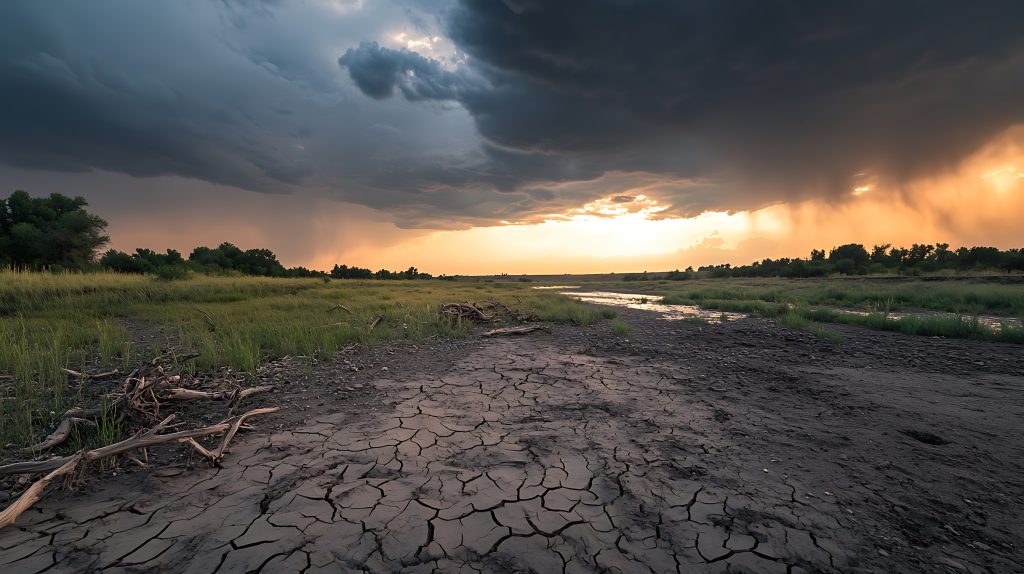
September is not only the beginning of the school year, but also an ideal opportunity to reconsider the challenges facing each of us. The beginning of 2025 was very dry – many regions of Poland experienced a lack of rain, rivers and lakes reached record lows, and farmers and gardeners struggled with water shortages. Such phenomena have become increasingly frequent in recent years, and forecasts indicate that drought could be one of the greatest challenges of the 21st century.
This year’s harvest has concluded. It’s a good time to review current practices and consider what we can do to improve soil health, increase drought resistance, and manage water more sustainably, as well as how to prepare for the next harvest. We discuss this with Patryk Kokociński, a farmer who irrigates his fields naturally, utilizing landscape retention water. Thanks to his efforts, the “Życie na Pola!” Association for the Protection of Mid-Field Landscape was also established.
A few hours of rain are enough for lawns to turn green and flowers to bloom. For this reason, many people believe that drought is an easily reversible problem, and that a week of heavy rain is enough to stave off a prolonged drought. However, hydrology isn’t so simple. Drought is a complex, multi-stage, and often hidden phenomenon, and its reversal depends not solely on the previous week’s weather. Short-term rainfall isn’t enough to address the consequences of drought. But what does effective “irrigation” actually look like?
The hydrological year, covering the period from November 1st to October 31st of the following year, is used to analyze the full cycle of water circulation in nature. This division takes into account autumn and winter rainfall and snowfall, which are stored in the environment, as well as spring thaw, which determines river flows, groundwater levels, and the retention capacity of land areas.
On Wednesday, August 7, 2024, Mateusz Balcerowicz – Deputy President of the State Water Holding Polish Waters signed a contract to implement the project “Review and update of the Drought Effects Counteracting Plan” (uDECP).
 PL
PL







