Stakeholders survey for the Plan to counteract the effects of drought
Implementation of the Plan to counteract the effects of drought is based on numerous sources of data, one of them is the stakeholder survey i.e. administration entities related to drought and risk management and water user groups who are at risk of this phenomenon and carry out activities including investments to reduce the effects of drought. The stakeholder survey was carried out from 17th December 2018 to 15th February 2019 and its main purpose was to collect data required for the development of the catalogue and actions programme to counteract the effects of drought. Respondents’ answers provided data and information covering inter alia:
- shortage of water resources,
- the range and periods of drought broken down by its 4 types i.e. atmospheric, agricultural, hydrological and hydrogeological drought,
- losses incurred as a result of a drought and costs incurred for actions taken by stakeholders to counteract the effects of drought,
- identification of economic, social and environmental areas most sensitive to the occurrence of the drought,
- actions implemented, currently being implemented and planned in the field of counteracting the effects of drought divided into actions listed in art. 184 par. 2 points 2) – 3) Water Law Act (Journal of Laws 2018 item 2268, with later changes),
- desired actions to counteract the effects of drought,
- documents, programmes determining the scope of activities or strategies related to preventing the effects of drought and / or other documents in force or being implemented as part of the activities of individual institutions or economic entities.
In total 3495 organizations in 5 stakeholder groups (presented in the diagram below) were invited to participate in the survey. The stakeholder survey structure, with a percentage representation, is depicted in the diagram below.
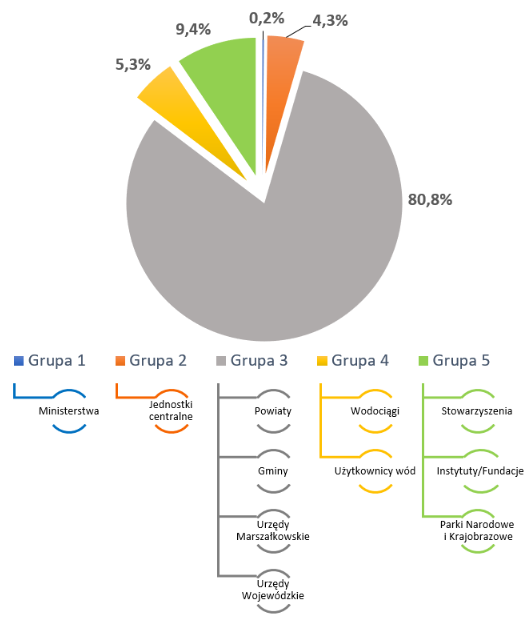
The final list of entities included in the statistics is the sum of the respondents originally invited to the survey together with entities registered under the given organization. The registration module allowed for the registration and completion of the questionnaire by a given entity as an unit operating within the organization, e.g. branches or individual departments. The number of respondents, together with entities submitted by organizations themselves, amounted to 3631. Among them, 2666 users replied to the survey (sum of online surveys and surveys sent via e-mail / post). The rate of return was achieved at the level of 73%. The highest rate of return was obtained in the group 3 – 80.3% and the lowest in the group 5 – 37.4%. The process of registration and filling in the questionnaires in sample subgroups of respondents can be traced on the animation below.
The results of the survey can be found in the Download Report HERE. Opens in a new window.
An overview of the main results is presented in the text under section – Survey results

Survey results
A. Drought and water shortages
The most often indicated type of drought was agricultural drought – over 49% of all indications (49.68%). Subsequently, the respondents indicated atmospheric drought – over 32% (32.74%) and hydrological drought – over 12% (12.7%). The hydrogeological drought accounted for only 4.88% of all indications of drought types. Agricultural drought was most often indicated in group 3 and hydrological in group 4 – water users and group 5 – Parks.
The highest number of answers indicating the occurrence of water shortages was obtained in the group 3-Marszałkowskie Offices – 85.71% of indications, Voivodship Offices – 75% and in Group 4 Water companies – 65.71%. Looking wider, the presence of water shortages was indicated by 56.26% of all respondents.
The aspects that this shortage concerned (the possibility of multiple choice) are:
in group 3, agriculture (1226 responses), water intake (460) and fish ponds (182);
in group 4 production (50 indications), water management (46) and municipal economy (40).
B. LOSSES AND COSTS AFFECTED BY DROUGHT
The key issue addressed in the surveyed questionnaire was the issue of effects caused by the drought, both in general and in detail, in relation to the losses suffered. The aspect most frequently mentioned by the respondents, which concerned the effects of drought, was the economic aspect 66.38% of responses, environmental / environmental aspect 19.44% and social only 14.18%.
The level of losses suffered was determined on 4-stage scale from imperceptible via perceptible, severe to catastrophic. The level of perceptible losses was indicated by 38.26% of respondents, the severe level was 31.61% and only 3.09% of respondents considered that the level of losses was catastrophic. The non-perceptible level of losses caused by drought was 27.04%.
Respondents, within the answers provided, most often indicated two sectors of the economy that experienced losses due to drought, ie: agriculture – plant production 40.15% of all responses and supply of water to people 17.85%, agriculture – irrigated 13.57% and fish ponds 8.53%. The aspect of impact of the effects of drought in the year of its occurrence was indicated by 66.67% of the group 4, and for a period of 2-3 years after the drought – by only 7.58%.
To analyse the losses and costs resulting from the drought, the question (in group 4) about the insurance policy against direct or indirect effects of this phenomenon was also taken into account. The answers received indicate that almost 70% (69.73%) of the surveyed water users do not have an insurance policy against the effects of drought. Only 5.5% of respondents declare that they do have the policy. The remaining 24.77% of respondents who answered this question indicated the option “not applicable”.
Appointing the commission to estimate damage to agricultural as a result of the occurrence of the drought phenomenon and estimating losses by these committees concerned 82.92% of respondents (question for group 3).
91.11% of respondents from group 3 indicated lack of additional costs of water supply during the drought. Only less than 9% (8.89%) of the replies confirmed that such costs were incurred. And the most frequently indicated type of operation was the delivery of water by watercars (70.59%).
The sum of reported costs related to supply of water to the population during the drought, from the respondents’ estimates, amounts to over PLN 19 million.
C. PROPOSED MEASURES TO COUNTERACT EFFECTS OF DROUGHT
As part of the survey questions, respondents were given the opportunity to report activities (investments) currently implemented / planned or desirable due to effects of drought in a given area, serving to counteract and reduce the negative effects of this phenomenon.
The vast majority of responses received – 72.76% – indicate that there is no need to implement measures to counteract the effects of drought (or constitutes information that the scope of the question does not concern the entity / institution). Only 27.24% of responses indicate the need to implement such activities.
Within the respondents of groups 2 and 3 (Communes, Poviats and Voivodship Offices) only 12% indicated the implementation or planning of activities related to the increase of natural or artificial retention. The most frequently indicated categories are: equipment or damming structures (230 indications), artificial reservoirs on flowing waters and objects associated with these reservoirs (111) and other categories (117).
Over 92% of respondents, within the groups mentioned above, inform about the lack of implementation of “soft” actions (any information, educational, promotional or scientific activities). Only 7.09% of responses indicated the implementation of such activities. Respondents most often indicated the implementation of tasks in the area of: educational activities (including workshops) – 95 indications, other activities – 83 indications, training – 59.
The desired actions have been defined in the survey as proposals of activities that have a particular potential for implementation due to the effects of the drought, and which are not currently planned for various reasons, e.g. financial or administrative. In total 946 indications of desired actions were given. The most frequently indicated category of desired actions are: devices and damming constructions – 219, artificial reservoirs on flowing waters and objects associated with these reservoirs – 106 and drainage devices (eg construction and reconstruction with change or / and addition of functions from drainage to irrigation) – 95.
Group 4 water users, including water companies, answered the question about investment / technological activities undertaken by the company in order to counteract the effects of drought. Over 30% of responses indicated that the company undertook investment activities to mitigate or counteract the effects of drought. 63.63% did not take any action, and nearly 5.5% indicated that the investment costs exceeded the amount of losses incurred and are unprofitable.
SURVEY DONE, WHAT IS NEXT?
The results obtained in the questionnaire are, for further work on the plan to counteract the effects of drought, a source of information on procedures, documents, plans and above all on activities and investments related to counteracting the effects of drought. The data collected in the survey, before being included in the catalogue and programme of measures to counteract the effects of drought, will undergo analytical procedures as part of the analysis of planning documents and programmes taking into account the aspect of reducing the effects of drought and work on identifying economic, social and environmental areas most sensitive to drought phenomena.
Full results of the survey can be found in the Download Report – Polish version HERE.


