33 years ago – on May 22, 1992, the Convention on Biological Diversity was held. Eight years later, in December 2000, the UN General Assembly commemorated this event by declaring May 22 as the International Day of Biological Diversity. This holiday aims to increase public awareness of biological diversity and its importance for socio-economic development. In 2025, the motto will be “Harmony with nature and sustainable development.”
Drought in Poland as a growing threat to ecosystems
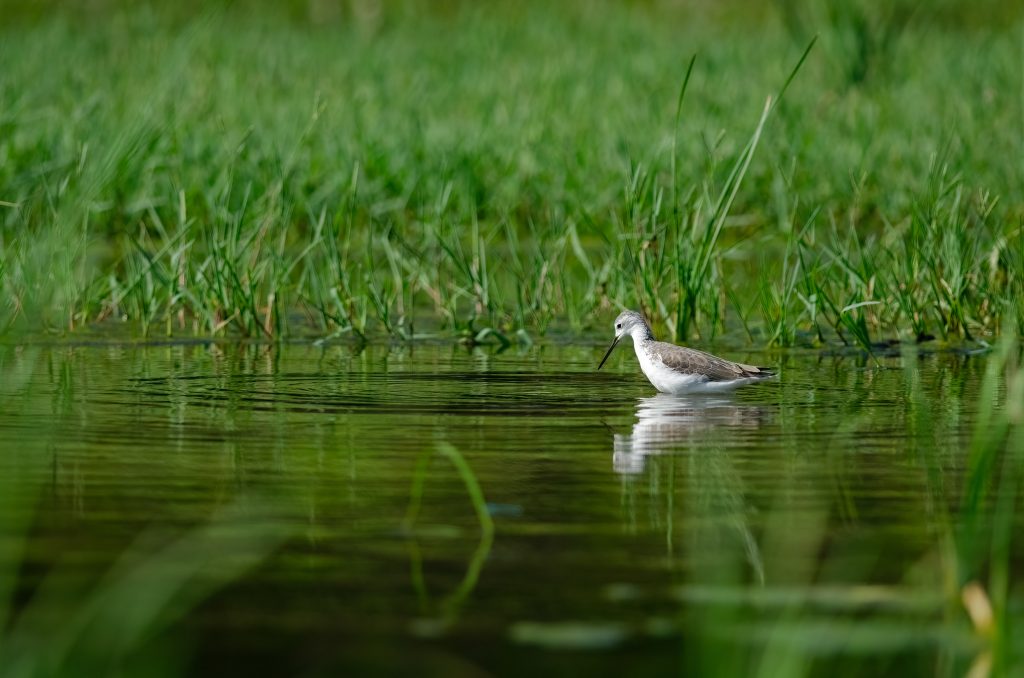
In recent years, we have been observing a deepening problem of drought in Poland. Due to climate change, water shortages, and rising annual temperatures, ecosystems are suffering significantly. The lack of water leads to their degradation. The phenomenon of drought affects, among others meadows, pastures and floodplain forests. For this reason, the populations of amphibians, invertebrates, and wetland birds are decreasing. In addition, long-term groundwater shortages cause the drying out of wetlands, which are extremely important for preserving biodiversity.
Biodiversity is the foundation of a stable environment. In order to maintain aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems in good condition, constant access to water is necessary. Poland is among the countries with one of the lowest water resources in Europe. This is only about 1,600 m³ of water per capita per year (with the European average of about 4,500 m³/person/year).
That is why retention, or the ability to periodically retain water, is so important today. The “Stop Drought! Start Retention!” campaign focuses on promoting solutions that will help minimize the effects of drought, and at the same time help support and maintain biodiversity in Poland. Among the most important actions in the context of counteracting the effects of drought and increasing biodiversity is increasing landscape retention, or generally speaking, retaining water where it falls. Landscape retention should also be understood as wetland retention. More information on small water retention can be found in the film from the WOW series, or All About Water – Small Water Retention.
There are four types of drought, one of which is hydrological drought. It means a long-term decrease in the water level in rivers and reservoirs. This phenomenon directly threatens habitats associated with water, such as wetlands (marshes, peat bogs, swamps), which are home to many species of plants and animals that we cannot find anywhere else. Therefore, we must remember to protect and restore them, including through renaturalization and reduction of river regulation, biological activation of oxbow lakes, elimination of fish migration barriers, and lake reclamation. All these activities will contribute to increasing biodiversity by protecting natural habitats of plants and animals.
Drought is a common problem and responsibility
Due to the fact that drought affects many areas and sectors of life (including increasing the threat to biodiversity) and is becoming more and more common, it is necessary to take action at both the local and national level. There are many ways to support the protection of biodiversity. Some of them are:
- Strict protection, i.e. protecting ecosystems from external influences, without interfering with natural processes.
- Protection in protected areas, i.e. creating protected areas, national and landscape parks.
- Active protection, which includes renaturalization of ecosystems, i.e. taking action to restore destroyed or degraded habitats, supporting programs to protect endangered species and restore their populations, as well as restoring natural functions of nature in degraded areas.
Each of us has a chance to contribute to reducing the negative impact of humans on the natural environment. Among these actions, we can distinguish the restoration of forests, protection of water sources from pollution, and control of greenhouse gas emissions. Education, support of local initiatives and promotion of sustainable development are also very important steps towards counteracting the effects of drought and protecting biodiversity.
Many actions should be taken at the state level. It is extremely important that we advocate for a sustainable agricultural policy, which consists of supporting ecological initiatives in agriculture and reducing the use of artificial fertilizers. In addition, as a state, we must protect areas of special natural importance. Poland must also invest in ecological technologies that will reduce energy consumption and the extraction of non-renewable sources. Every regulation and provision on industrial activity that will help us protect nature will contribute to a better tomorrow.
Small steps, big changes in nature protection
Actions at the local level are equally crucial. Let’s remember that each of us can propose a civic initiative supporting ecosystems in our immediate surroundings, such as cleaning up nearby rivers. Additionally, we should focus on creating urban greenery that supports biodiversity and helps counteract climate change and the effects of drought. Examples of blue-green infrastructure include: retention ponds, infiltration ditches, rain gardens, green bus stops, roofs, facades and walls, as well as permeable surfaces. You can find additional examples in our brochure “How to retain water in a single-family home and in public spaces.”
Celebrating the International Day of Biological Diversity is an excellent opportunity to remind ourselves that each of us has an impact on the state of the environment. Appropriate daily activities, as well as raising awareness of residents about nature conservation and sustainable development, will help mitigate the effects of drought and support Poland’s biodiversity. On our website, you will find even more examples and inspiration on how to take care of water management and related ecosystems.
Together, let’s say “Stop Drought! Start Retention!”
 PL
PL

